Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes Mechanism
C 3 H 6. Basically it follows a 3-step mechanism.
Addition Of Hydrogen Halides To Alkenes Chemgapedia
These include S N 1 and E1 reactions of alkyl halides and Brønsted acid addition reactions to alkenes.

. Alkenes having four or more carbon atoms can form diverse structural isomersMost alkenes are also isomers of cycloalkanesAcyclic alkene structural isomers with only one double bond follow. The resulting benzyne forms addition products usually by nucleophilic addition and protonation. Mechanism of Dehydration of Alcohols.
Generation of the benzyne intermediate is the slow step. C 4 H 8. Dehydration of alcohols follows the E1 or E2 mechanism.
The steps that are involved. Thus the process is formally analogous to the E1cb mechanism of aliphatic compounds. 1-butene 2-butene and isobutylene.
The cation may transfer a proton to a base giving a double. Aryl bromides and iodides on the other hand generally appear to undergo elimination by a concerted syn-coplanar E2 mechanism. C 2 H 4.
Formation of alkenes. The cation may bond to a nucleophile to give a substitution or addition product. C 5 H 10.
The primary alcohols elimination reactions follow the E2 mechanism whereas the secondary and tertiary alcohols elimination reaction follows the E1 mechanism. To summarize when carbocations are formed one can expect them to react further by one or more of the following modes.

Electrophilic Addition Of Hydrogen Halides To Alkenes Youtube
Addition Of Hydrogen Halides To Alkenes Chemgapedia
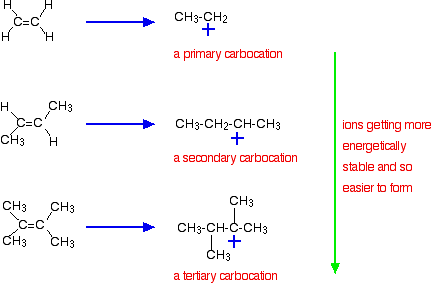
9 2 Addition Of Hydrogen Halides To Symmetrical Alkenes Chemistry Libretexts
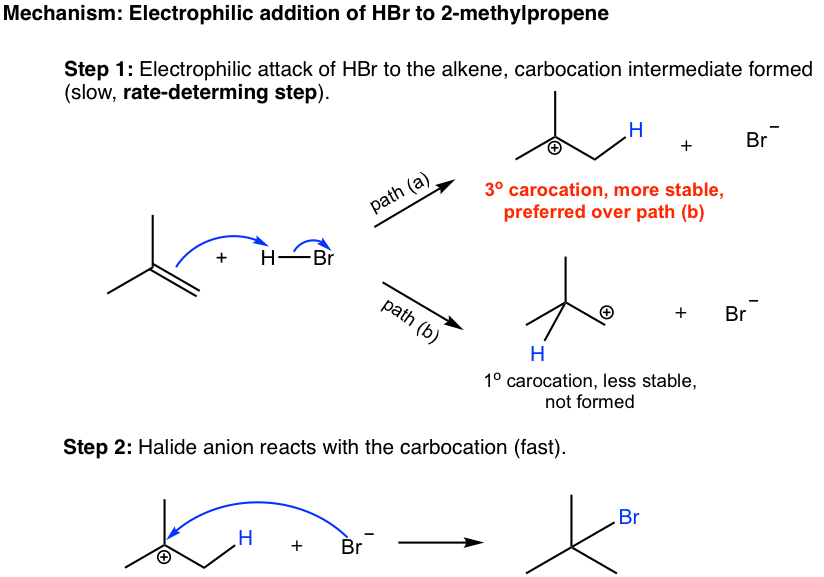
10 2 Reactions Of Alkenes Addition Of Hydrogen Halide To Alkenes Organic Chemistry I
No comments for "Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes Mechanism"
Post a Comment